Table Of Content
What Is Staking in Crypto?
Staking in crypto is the process of locking up your cryptocurrency in a blockchain network to help validate transactions and maintain security. In return, you earn staking rewards—similar to earning interest on a savings account.
Staking is available on proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchains like Ethereum, Cardano, and Solana, and has become a popular way to earn passive income while supporting decentralized networks.
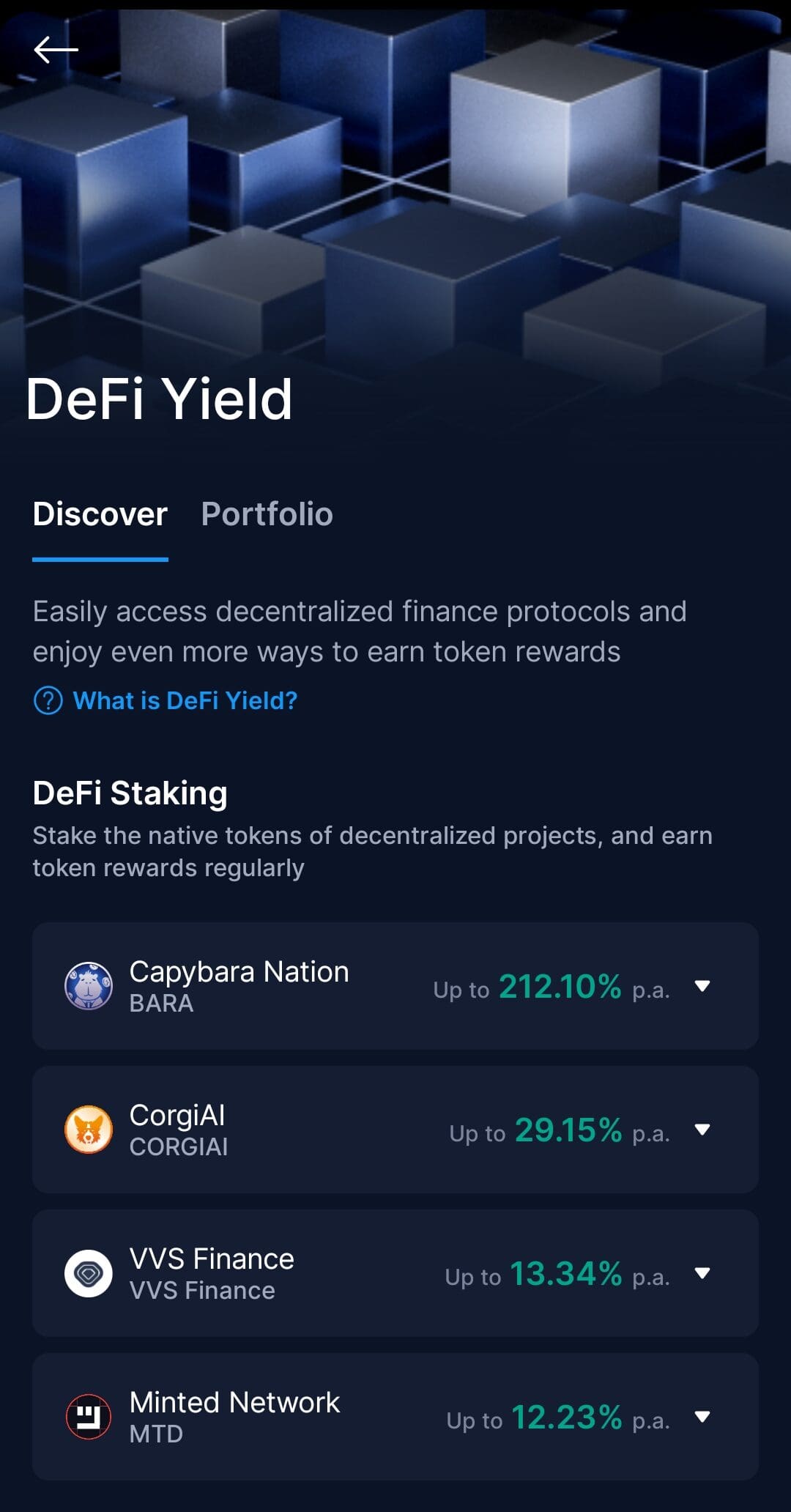
How Does Staking Work?
In order to participate in staking, you either stake directly or delegate your coins to a validator node. Here's how the process typically works:
Locking Up Tokens: You commit a specific amount of cryptocurrency (e.g., ETH, ADA) to the network for a fixed or flexible period. These assets remain in your wallet or with a validator but are temporarily inaccessible for trading.
Participating in Network Security: Your staked crypto helps validate transactions and secure the blockchain. As a result, you're contributing to decentralization and the efficiency of the network.
Earning Rewards: Validators (or delegators) receive rewards in the form of additional crypto, typically based on the amount staked and the length of time held.
Unstaking Period: Many platforms impose an unbonding period before you can access your tokens again. For example, unstaking from Ethereum may take several days due to network queues.
Platforms like Coinbase and Kraken offer built-in staking features, making it easier for beginners to get started without running a validator node.
Risks of Staking
Staking offers steady rewards, but it’s not risk-free. In order to stake wisely, it’s important to understand the main risks involved—and how to minimize them:
-
Slashing Penalties
If your validator breaks protocol rules—such as double signing or going offline—your staked funds may be partially slashed (i.e., destroyed).
This is especially true on blockchains like Ethereum and Cosmos.
To reduce this risk, choose a validator with a strong uptime record and no history of slashing. Tools like Rated Network can help assess validator performance.
-
Lockup and Liquidity Risk
Many staking platforms require a lockup period (e.g., 7–21 days), which means you can’t immediately sell your crypto if prices fall. Ethereum, for instance, has a variable withdrawal queue.
To avoid this, consider using platforms with liquid staking options like Lido or Rocket Pool, which give you a tradable token in return.
-
Platform or Custodial Risk
If you stake using a centralized exchange (e.g., Binance, Coinbase), you’re handing over control of your private keys. If the platform is hacked or mismanages funds, your assets may be at risk.
To stay safer, consider using non-custodial wallets or decentralized staking protocols that let you retain full control over your crypto.
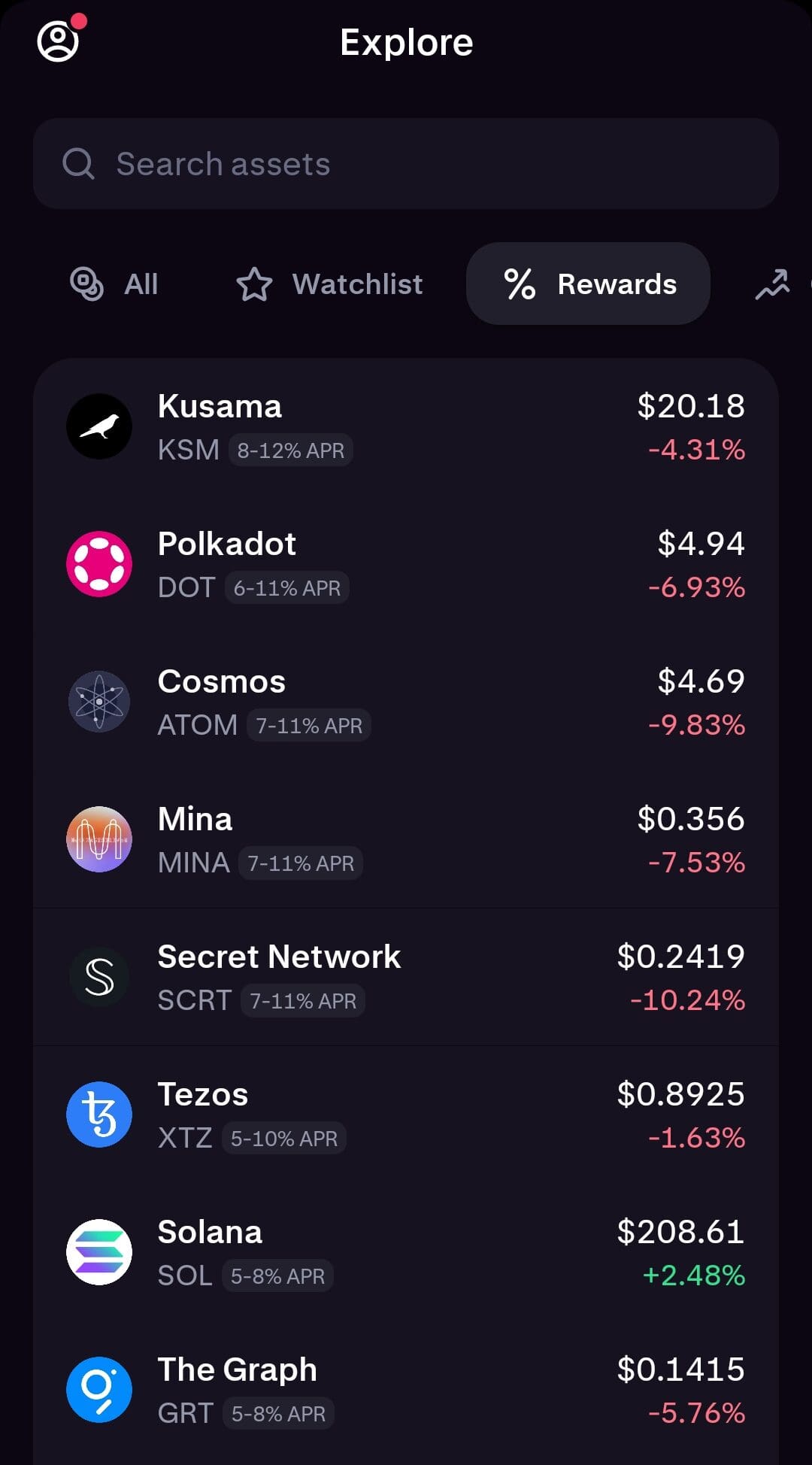
Top Cryptocurrencies You Can Stake
Many proof-of-stake coins offer staking rewards, making them attractive for long-term holders looking to earn passive income:
Ethereum (ETH): After its shift to proof-of-stake, ETH staking offers steady rewards but requires careful consideration of lock-up periods and validator risks.
Cardano (ADA): Known for its energy efficiency, ADA staking is popular because there is no lockup period, allowing users to withdraw at any time.
Solana (SOL): SOL staking offers competitive rewards, but users must choose validators carefully due to the network's previous downtime.
Polkadot (DOT): Offers high yields and supports nomination pools, making it easier for smaller holders to participate.
Staking opportunities vary by blockchain, so it’s important to research the specific rules and risks.
Top Platforms for Crypto Staking
Crypto users can stake through exchanges or decentralized services depending on their technical skill and security preferences:
Coinbase: Ideal for beginners, Coinbase offers simple staking options for ETH, ADA, SOL, and more—but with relatively high fees.
Binance: Offers flexible and locked staking on a wide variety of coins, along with detailed reward calculators and estimated APRs.
Lido: A leading liquid staking protocol for Ethereum and Solana that gives users tradable tokens like stETH while earning staking rewards.
Kraken: Offers transparent staking for over 10 cryptocurrencies and includes an “unstaking” feature for added flexibility.
Each platform differs in reward rates, fees, and lock-up terms.
Summary: Is Crypto Staking Safe & Profitable?
Staking remains a viable strategy for earning passive income in 2025, especially as major blockchains like Ethereum and Solana continue to mature. It can be profitable, but also involves risks like slashing, validator failure, or platform security.
Therefore, investors should balance convenience with control, and consider using trusted validators or decentralized protocols.
FAQ
Mining uses computational power to validate transactions (proof-of-work), while staking uses locked crypto to secure networks (proof-of-stake).
Yes, you could lose funds due to slashing penalties, validator errors, or platform hacks—especially if you're not using a trusted method.
Yes. Each blockchain has its own reward structure, typically ranging from 3% to over 15% annually depending on demand and inflation models.
It depends on the network. Some blockchains like Cardano offer flexible unstaking, while others like Ethereum have waiting periods.
In many countries, staking rewards are taxable as income when received. Always consult local tax laws or a crypto tax advisor.
Liquid staking lets you earn staking rewards while still being able to trade a tokenized version of your staked crypto, like stETH or mSOL.
Not necessarily. Centralized platforms and staking pools make it easy to stake without running your own validator node.
Staking through wallets gives you more control and often lower fees, but exchanges are simpler for beginners.
